3D Printing Technology has emerged as a game-changer in the world of manufacturing. What started as a tool for rapid prototyping has now grown into a technology with far-reaching implications across various industries. From healthcare to aerospace, this cutting-edge approach is redefining how products are designed, created, and distributed. In this article, we will explore how 3D Printing Technology works, its benefits, challenges, and the potential it holds for the future.
Understanding 3D Printing Technology
What is 3D Printing?
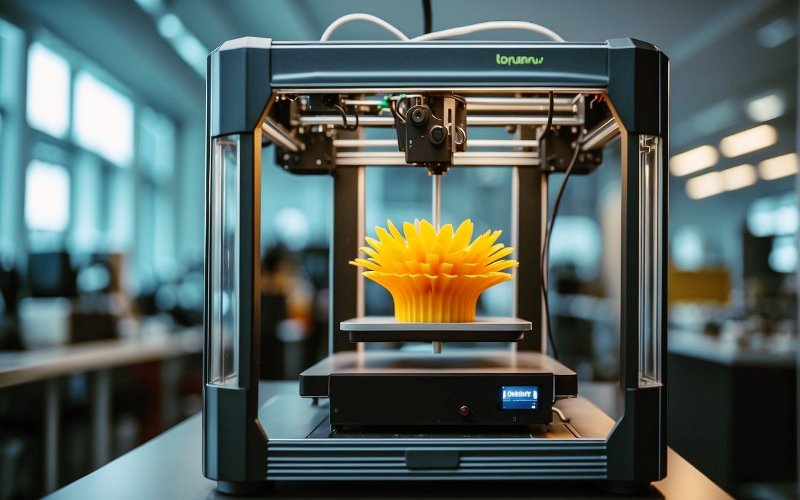
At its core, 3D Printing Technology, also known as additive manufacturing, is the process of creating a three-dimensional object from a digital design. Unlike traditional manufacturing, which often involves cutting material away, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, using materials like plastic, resin, or metal. This process allows for the creation of highly complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional methods.
How Does 3D Printing Technology Work?
The journey of 3D Printing Technology begins with a digital design file, typically created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This file is then processed by slicing software, which divides the object into thin layers. The printer reads these layers and deposits material, one layer at a time, to form the final object. Different types of printers, such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) and Stereolithography (SLA), use varying methods and materials to achieve the finished product.
The Evolution of 3D Printing Technology
A Brief History
Since its inception in the 1980s, 3D Printing Technology has come a long way. Initially limited to rapid prototyping, it has evolved into a tool for full-scale production in industries like automotive and aerospace. Early machines were slow and expensive, but today’s printers are faster, more affordable, and capable of working with a broader range of materials, including metals and ceramics.
Key Applications of 3D Printing Technology
- Healthcare: Medical professionals are using 3D-printed models to plan surgeries and create customized prosthetics, dental implants, and even bioprinted organs.
- Aerospace: Lightweight, durable parts for aircraft and spacecraft are being manufactured using 3D Printing Technology, offering significant cost reductions and improved fuel efficiency.
- Automotive: The automotive industry is leveraging 3D printing to produce prototypes quickly and manufacture parts tailored to specific vehicle models.
The Benefits of 3D Printing Technology
Reducing Waste
One of the most significant advantages of 3D Printing Technology is its ability to minimize waste. Traditional manufacturing methods often involve cutting away material, resulting in substantial waste. In contrast, 3D printing uses only the necessary amount of material, making it an eco-friendly alternative to conventional manufacturing.
Speed and Flexibility
Another key benefit is the speed at which products can be produced. With traditional manufacturing, developing a prototype or custom part can take weeks, if not months. 3D Printing Technology speeds up the process, enabling the production of parts within days. Additionally, the layer-by-layer approach allows for intricate designs and customized products that are difficult to achieve with traditional methods.
Industries Embracing 3D Printing Technology
Healthcare and Medical Applications
In healthcare, 3D Printing Technology is making personalized medicine a reality. Surgeons can use 3D-printed models to practice complex surgeries, while prosthetic devices and implants can be customized to fit a patient’s specific needs. This technology is also making waves in bioprinting, where scientists are working toward printing functional human organs.
Automotive and Aerospace Sectors
Car manufacturers are using 3D printing to create specialized parts, while the aerospace industry is producing lighter and stronger components. By reducing the weight of parts, 3D Printing Technology is improving fuel efficiency and reducing costs, making it a valuable asset in these industries.
Construction and Consumer Goods
In construction, large-scale 3D printers are being used to build homes more efficiently. Additionally, consumer goods like custom jewelry, shoes, and household items are being tailored to individual specifications, thanks to 3D Printing Technology.
The Environmental Impact of 3D Printing Technology
A Sustainable Alternative
As sustainability becomes a growing concern, 3D Printing Technology is being recognized for its positive environmental impact. By using only the materials required for each object, it significantly reduces waste. The ability to print items on demand also eliminates the need for mass production and storage, reducing energy consumption and resource use.
Use of Recycled Materials
Innovators are finding ways to make 3D printing even greener by using recycled materials. For example, companies are developing 3D printers that can work with recycled plastics, transforming waste into new, useful products.
Challenges of 3D Printing Technology
High Material Costs
While 3D Printing Technology offers many benefits, it’s not without its challenges. One of the most significant barriers is the high cost of materials, particularly when using metals or specialized polymers. For large-scale production, traditional manufacturing methods are still often more cost-effective.
Quality Control
Another issue is the inconsistency in quality that can sometimes arise with 3D printing. Ensuring that parts meet industry standards, especially in critical fields like healthcare and aerospace, is essential but can be challenging with 3D-printed components.
The Future of 3D Printing Technology
Bioprinting and Healthcare
The future of 3D Printing Technology is bright, with ongoing advancements poised to expand its applications even further. Bioprinting, which involves printing functional human organs, is an area of particular interest. Scientists are already making progress, and one day, it may be possible to print organs for transplants, eliminating the need for donors.
Space Exploration
In space exploration, 3D Printing Technology could play a crucial role in building habitats and infrastructure on other planets. NASA has already experimented with 3D printing aboard the International Space Station, and future missions may rely on 3D printing to produce tools and structures in space.
Conclusion: The Lasting Impact of 3D Printing Technology
3D Printing Technology is no longer just a tool for prototypes—it’s a full-fledged manufacturing solution with the potential to revolutionize industries across the board. Its ability to produce complex, customized objects with minimal waste is driving innovation in healthcare, aerospace, automotive, and beyond. As the technology continues to evolve, its applications will only expand, shaping the future of manufacturing for generations to come.
Also visit on techitl.com.